How to Use Curl or Postman to Interact With a MCP Server
I wanted to understand how the data and transport layers work in MCP. To do that, I mimicked what a MCP client would do by using curl and then Postman to connect to a MCP server. This allowed me to step through the lifecycle of a connection and get a peek into how messages are exchanged via JSON-RPC.
Overview
MCP clients will handle client-server connections for you but what is actually happening?
The MCP docs state that:
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) defines a rigorous lifecycle for client-server connections that ensures proper capability negotiation and state management.
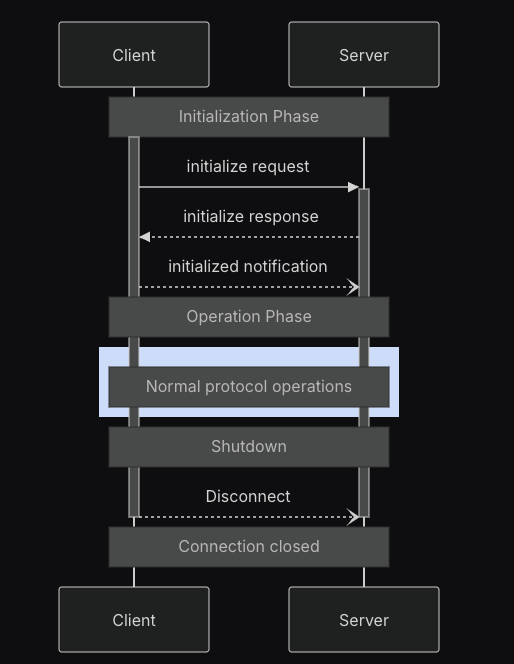
Using curl and Postman, I was able to get a better sense of what happens in the initialization and operation phases (see diagram above).
The following guide assumes you:
- have access to
curlor Postman - have a MCP server running at
http://127.0.0.1:8000 - exposed a MCP endpoint at
/mcp
curl
Send Initialize Request
# Save the response headers to get the session ID
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8000/mcp \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Accept: application/json, text/event-stream" \
-D headers.txt \
-d '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "initialize",
"params": {
"protocolVersion": "2024-11-05",
"capabilities": {
"tools": {},
"resources": {},
"prompts": {}
},
"clientInfo": {
"name": "curl-client",
"version": "1.0.0"
}
}
}'
The server responds immediately with initialization details:
event: message
data: {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
"protocolVersion": "2024-11-05",
"capabilities": {
"tools": {
"listChanged": false
},
"resources": {
"subscribe": false,
"listChanged": false
},
"prompts": {
"listChanged": false
}
},
"serverInfo": {
"name": "Demo",
"version": "1.12.3"
}
}
}
Extract the Session ID
# Extract the session ID from headers
SESSION_ID=$(grep -i "mcp-session-id" headers.txt | cut -d' ' -f2 | tr -d '\r')
echo "Session ID: $SESSION_ID"
Send Initialized Notification
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8000/mcp \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Accept: application/json, text/event-stream" \
-H "Mcp-Session-Id: $SESSION_ID" \
-d '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "notifications/initialized"
}'
Operational Communication
Once initialized, you can immediately send operational requests. Each request receives an immediate response.
List Available Tools
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8000/mcp \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Accept: application/json, text/event-stream" \
-H "Mcp-Session-Id: $SESSION_ID" \
-d '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"method": "tools/list"
}'
Response includes all available tools with their schemas:
event: message
data: {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"result": {
"tools": [
{
"name": "add",
"description": "Add two numbers",
"inputSchema": {
"properties": {
"a": {
"title": "A",
"type": "integer"
},
"b": {
"title": "B",
"type": "integer"
}
},
"required": [
"a",
"b"
],
"type": "object"
},
"outputSchema": {
"properties": {
"result": {
"title": "Result",
"type": "integer"
}
},
"required": [
"result"
],
"type": "object"
}
}
]
}
}
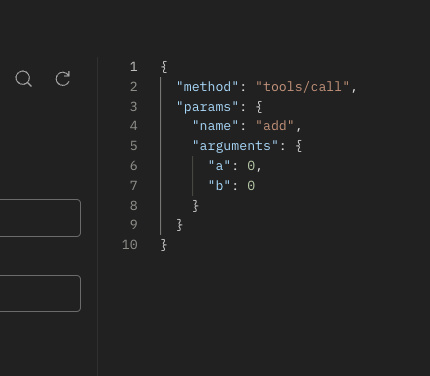
Call a Tool
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8000/mcp \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Accept: application/json, text/event-stream" \
-H "Mcp-Session-Id: $SESSION_ID" \
-d '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 3,
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {
"name": "add",
"arguments": {
"a": 5,
"b": 3
}
}
}'
Session Management
Streamable HTTP handles session management differently than SSE:
- No explicit session IDs: The server may use connection-based or stateless session management
- Optional session headers: Some servers support
Mcp-Session-Idheaders for explicit session tracking - Immediate responses: All responses come back in the same HTTP request
Postman
The following illustrates how to create a MCP request as described in the Postman documentation.
Click New
Select MCP
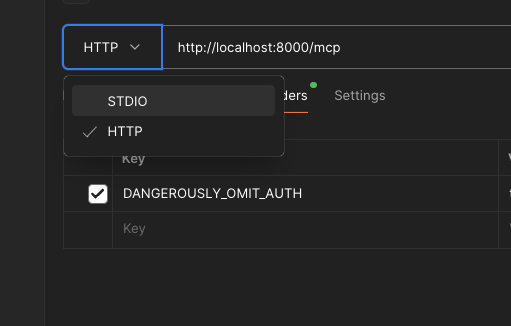
Select Transport
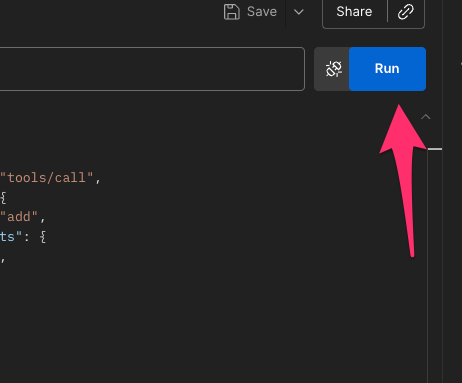
Click Run
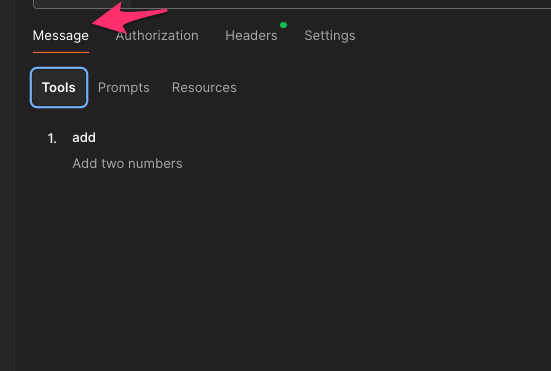
See what Tools are Available
See the actual JSON-RPC message that was sent when executing a tool